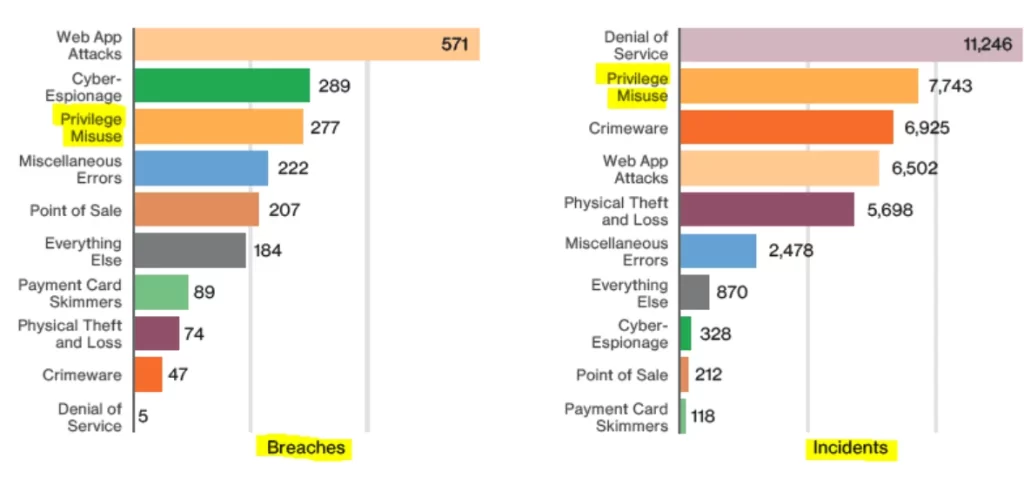
According to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report, 82% of data breaches had some type of human involvement whether in the form human error, social engineering attacks or privilege abuse. System intrusion is the biggest reason behind privilege misuse followed by lost and stolen credentials.
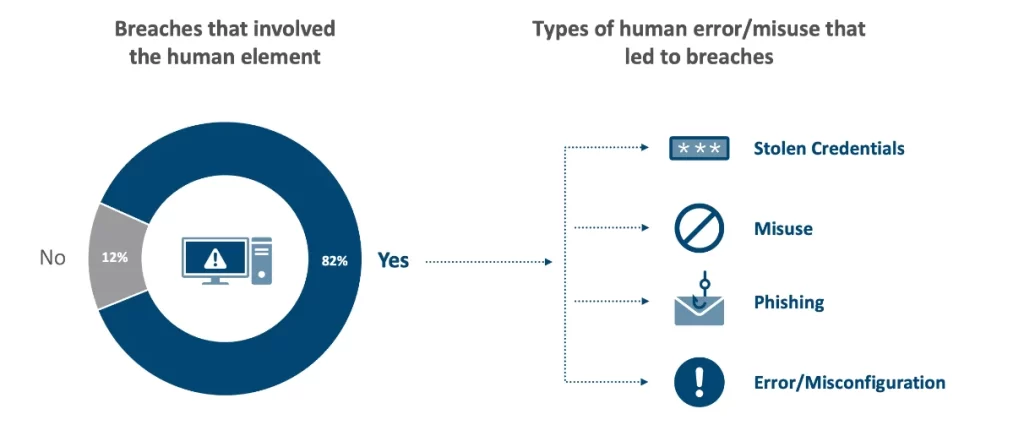
When it comes to industries, healthcare is one of the worst affected with 19% share while retail industry is at the second spot with 13.7% while professional and manufacturing shares the third position with 13% share. What’s most surprising is the fact that finance and information technology ranked at fourth and fifth position with 11.6% and 8.9% share respectively.
This article will teach you everything you need to know about privilege abuse.
Privilege Abuse: Everything You Need To Know In Order To Stop It
What is Privilege Abuse?
Privilege abuse is a malicious attempt to penetrate a network by gaining access to privileged accounts with the intention of stealing sensitive business data so they can attack the organization or profit from it by selling it on the dark web. Privileged accounts have access to information traditional accounts can’t. This means that if cyber criminals manage to compromise privileged accounts, they can make the most of the additional accessibility these accounts have.
How Privileges Can be Misused By Authorized Users?
Since users with access to privileged accounts have a higher level of accessibility to organization-sensitive data, they can misuse these privileges as well. These authorized users can use a number of different tactics such as:
- Account manipulation
- Abusing administrative accounts
- Misusing service accounts
- Turning off account abuse checks
Account manipulation is the most commonly used tactic. Once the attacker gains access to a privileged account, they might perform tasks just like a normal user to evade detection but later target an active directory to make changes to the account settings to gain access to other systems on the same network.
Another technique hackers use when they get access to a privileged account is that they either inject malicious code or execute malicious software to cause even more damage by launching dangerous cybersecurity attacks. This can not only extend your financial losses but can also put your entire security infrastructure at risk.
What Methods Do Insiders Use For Privilege Misuse?
There are instances when an insider or internal threat actor might be involved in privilege abuse. In such circumstances, the methods used are completely different from the external threat actors. Insiders usually used one of the following tactics for privilege abuse.
- Shoulder surfing
- Brute force attack
- Password spraying
- Dictionary attacks
- Credential stuffing
- Pass the hash attack
To give you a better idea about each one, let’s look at each one in more detail.
- Shoulder surfing
In this technique, the threat actor closely monitors the user until he or she reveals their credentials to them.
- Brute force attack
As the name suggests, a brute force attack exhausts all the possible combinations to find the real password.
- Password spraying
In password spraying, attackers use specialized tools to identify common trends and patterns as well as commonly used passwords to compromise those accounts.
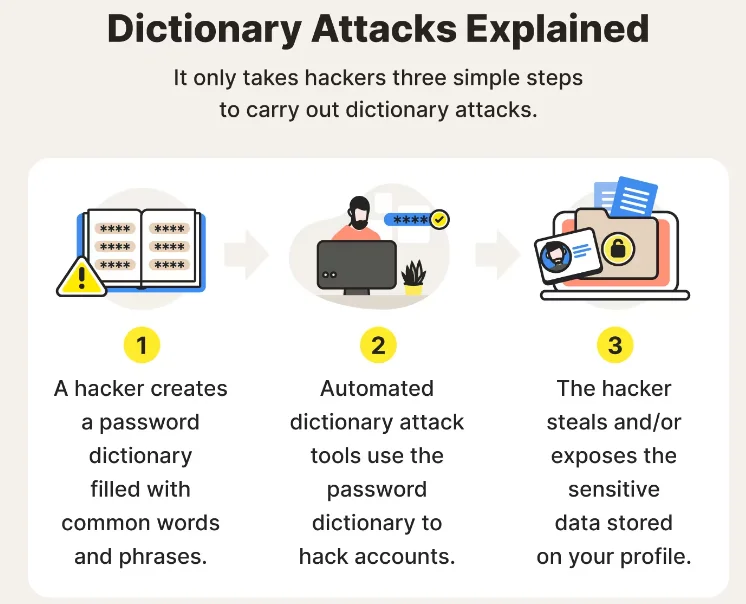
- Dictionary attacks
In a dictionary attack, the attacker creates a list of possible passwords with the help of software which is then used to log to privilege accounts
- Credential stuffing
Hackers try to get access to privileged accounts via stolen credentials and older data breach incidents. Next, they start sending login requests by using those stolen credentials and records on different websites. If your privileged users use the same passwords to log in to different accounts and passwords then hackers can also gain access to those accounts as well.
- Pass the hash attack
Pass the hash attack enable cybercriminals to bypass the authentication check without entering a password. Instead of using a password, they use a NT LAN manager for authentication purposes. This allows them to gain access to privileged accounts without requiring a password.
How To Prevent Privilege Abuse?
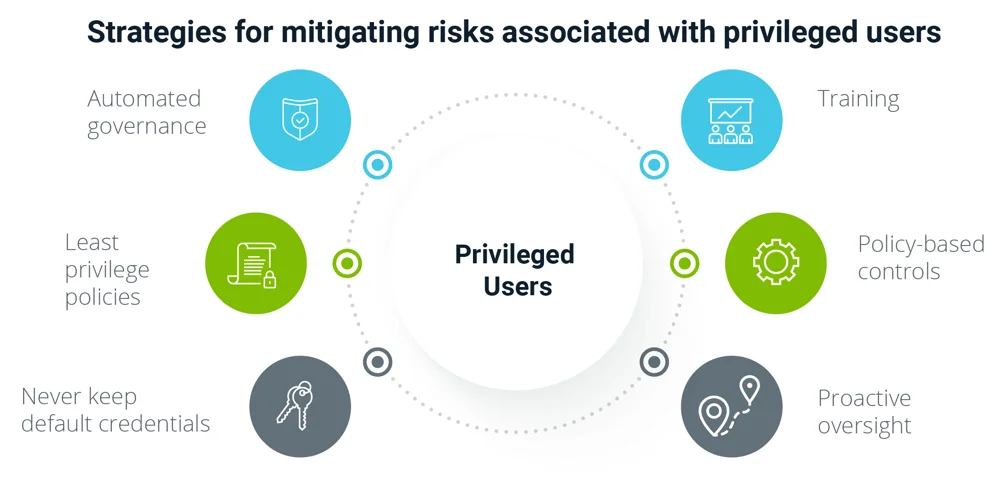
Now that you know what privilege abuse is, how it works, and what methods threat actors both insiders and outsiders use, it is time to look at ways to prevent privilege abuse.
- Identify user roles and access profiles
- Make sure all these roles and profiles align with cybersecurity protocols and standards
- Implement zero trust
- Create an access granting process that can easily be audited which also allows you to add and remote steps according to your business needs
- Closely monitor all the privileged access users and their activities
- Track behavior of privileged users in real time
In addition to taking all these steps, you can also invest in an identity and access management system or a privilege access management system. These solutions offer some handy features such as dynamic password controller, multi factor authentication, privilege session manager and dynamic data masking to name just a few. Some even come preloaded with database access managers telling businesses who is accessing your databases when. Advanced privilege access management system also harnesses the power of automation for automating privilege tasks.
Having real time tracking capabilities for privilege accounts is critical. You don’t want to be knowing about malicious activity when the damage has already been done. You should be alerted to the warning signs and even the suspicious behavior so you can detect privilege abuse early and do something about it. The longer it takes for you to respond, the more time the attacker will get to wreak havoc on your cybersecurity infrastructure.
Assign roles and access based on the nature of work. If someone requires access to a particular document to complete their task, he or she should have access to that document only. By following the principle of least privilege, you can minimize the risk.
What steps do you take to prevent privilege access abuse in your organization? Share it with us in the comments section below.





Add comment