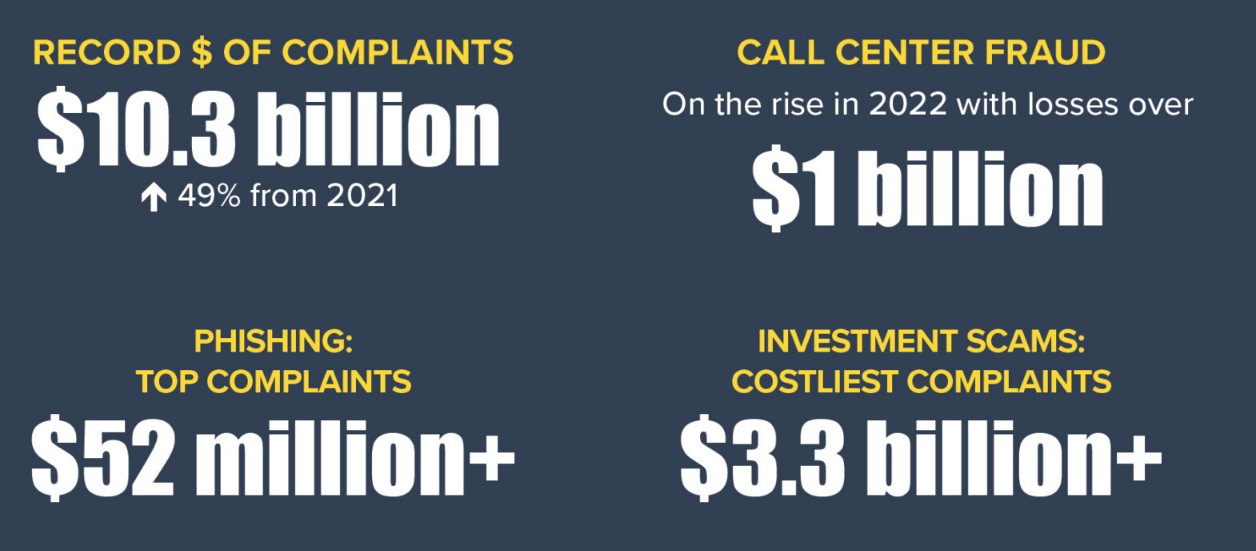
The FBI’s latest Internet Crime Report underscores the critical link between cyber risk and business risk, as well as the inseparable nature of cybersecurity and national security. The report reveals that cyber crime losses have skyrocketed to an astounding $10 billion, surpassing the previous year’s figure of $6.9 billion.
The year 2022 witnessed a concerning surge in cyber crime-related complaints, as reported by the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) of the FBI. With over 800,000 complaints registered, the scale of the issue highlights the increasingly alarming threat landscape.

These figures represent a concerning trend, as it reflects the increasing financial impact cyber criminals have on various sectors. The significant losses underscore the pressing need for organizations and individuals to prioritize cybersecurity and fortify their defenses against evolving threats.
In this article, you will learn about seven key takeaways from the FBI internet crime report.
- 5 Most Common Types of Internet Crimes
- 7 Key Takeaways From FBI Internet Crime Report
- 1. Phishing Is Still The Biggest Threat
- 2. Personal Data Breaches Comes At The Second Spot
- 3. Ransomware Attacks Are Evolving
- 4. Social Engineering Attack Turn on A New Leaf
- 5. Business Email Compromise
- 6. Crypto, Real Estate and Jobs Scams
- 7. Call Center Fraud
- Summary
5 Most Common Types of Internet Crimes
The top five cyber crime types reported in 2022 shed light on the prevalent threats faced by individuals and organizations alike. Phishing topped the list with 300,497 complaints, followed by personal data breaches (58,859), non-payment or non-delivery scams (51,679), extortion schemes (39,416), and tech support fraud (32,538).

Additionally, the FBI’s report highlighted other significant threat overviews, including business email compromise (BEC), investment scams, ransomware attacks, and call center fraud.
7 Key Takeaways From FBI Internet Crime Report
Here are seven key takeaways from the FBI internet crime report.
1. Phishing Is Still The Biggest Threat
According to the FBI’s report, phishing continues to be the biggest threat in the cybercrime landscape. During the year 2022, there were 300,497 complaints regarding phishing attacks. Cybercriminals employ various deceptive techniques to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or executing malicious actions. Phishing attacks remain a prominent avenue for data breaches and financial losses, highlighting the need for enhanced user awareness and cybersecurity measures.
2. Personal Data Breaches Comes At The Second Spot
Personal data breaches have become the second biggest threat in the realm of cybersecurity, as highlighted by 58,859 complaints reported by the FBI. Regular assessments for vulnerabilities and simulated attacks (penetration testing) are also crucial to identify and rectify any weaknesses in the security infrastructure.
3. Ransomware Attacks Are Evolving
In 2022, the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) received 2,385 complaints classified as ransomware, resulting in adjusted losses exceeding $34.3 million. The most common initial infection vectors reported were phishing, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) exploitation, and software vulnerabilities. To protect against these attacks, businesses and individuals should maintain up-to-date software and systems, enforce strong access controls, and educate employees on identifying phishing attempts.
The top five sectors affected by ransomware, according to the IC3, were
- Healthcare
- Critical Manufacturing
- Government Facilities
- Information Technology
- Financial Services

The three most prevalent ransomware variants reported were
- Lockbit with 149 incidents
- ALPHA/BlackCat with 114 incidents
- HIVE with 87 incidents
However, it is crucial to note that the FBI strongly discourages paying ransoms as it may encourage further attacks, support criminal activities, and does not guarantee file recovery for the victims.
4. Social Engineering Attack Turn on A New Leaf
Social engineering attacks involve manipulating individuals into revealing confidential information or performing actions that may compromise security. These attacks are becoming more targeted and personalized, making them harder to detect.
5. Business Email Compromise
Business Email Compromise (BEC) involves impersonating executives or employees to deceive individuals into performing unauthorized actions or transferring funds. BEC attacks have seen a rise in recent years and can result in substantial financial losses for organizations.
In 2022, the IC3 recorded a total of 21,832 complaints related to Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams, resulting in losses exceeding $2.7 billion. BEC scams involve fraudsters employing social engineering or hacking techniques to gain unauthorized access to legitimate business email accounts, enabling them to carry out unauthorized fund transfers. The ongoing battle between threat actors and security teams has led to the evolution of BEC scams.

Previously, these schemes primarily relied on compromised vendor emails, W-2 information requests, real estate sector scams, or the solicitation of large amounts of gift cards. However, more recently, attackers have increasingly targeted custodial accounts held at financial institutions for cryptocurrency exchanges. They may also instruct victims to directly send funds to cryptocurrency platforms, where the funds can be rapidly dispersed.
Notably, the IC3 observed a subtle shift in the types of targets being exploited by BEC scams last year. In addition to traditional banking accounts, actors now focus on victims’ investment accounts. Furthermore, malicious individuals are increasingly utilizing spoofed legitimate business phone numbers to authenticate fraudulent banking transactions.
6. Crypto, Real Estate and Jobs Scams
As cryptocurrencies gain popularity, cybercriminals are capitalizing on this trend by devising scams that exploit unsuspecting investors. The article sheds light on the increasing prevalence of cryptocurrency scams and highlights the risks associated with investing in unverified platforms. Additionally, it explores the emerging threats in the real estate and job sectors, where fraudsters exploit individuals seeking opportunities or attempting to purchase properties.

7. Call Center Fraud
Call center fraud involves criminals impersonating legitimate organizations and contacting individuals to extract sensitive information or carry out fraudulent activities. These scams exploit trust and often target vulnerable individuals, such as the elderly.
Summary
FBI Internet Crime Report highlights the alarming increase in cybercrime losses, reaching a staggering $10 billion. The findings demonstrate a significant rise compared to previous years, emphasizing the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. The report identifies various factors contributing to this surge, including sophisticated attack techniques, increased reliance on digital technologies, and inadequate security practices. The study’s findings emphasize the urgent need for organizations and individuals to prioritize cybersecurity, invest in robust defense mechanisms, and educate themselves on best practices to mitigate the escalating risk of cybercrime.





Add comment