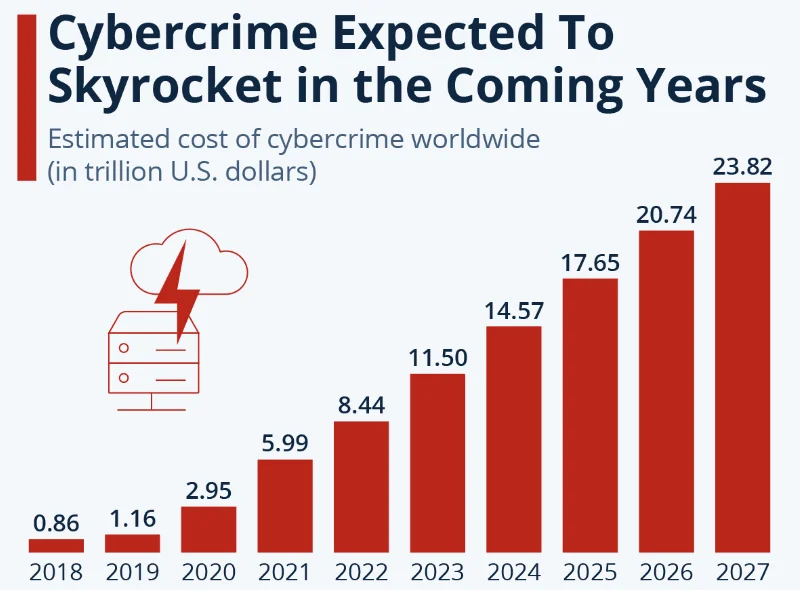
Deep Instinct’s recent Voice of SecOps Report, based on a survey of 652 senior cybersecurity experts from large companies, highlights a concerning surge in global attacks due to threat actors leveraging generative AI. Over the past year, such AI-powered attacks have significantly escalated, underscoring the growing sophistication of cybercriminal tactics.
The study also highlights a notable shift in data security strategies, driven by the pressing threat of ransomware. A rising number of organizations are now willing to pay ransoms to regain control after falling victim to attacks. However, this changing landscape is taking a toll on cybersecurity teams, leading to heightened stress levels and burnout.

The report’s findings mirror a wider concern over the potential risks associated with generative AI, and despite efforts to combat ransomware, its persistence remains a significant concern as attackers target new vulnerabilities and engage in data theft. Stress levels among security professionals have even reached levels similar to those witnessed during the mid-COVID pandemic period.
Deep Instinct’s report points out a sharp rise in global attacks powered by generative AI, emphasizing the evolving threat landscape. Organizations’ responses to ransomware are shifting, with a greater willingness to pay ransoms. Nonetheless, this evolving scenario is straining cybersecurity teams, leading to increased stress levels and the contemplation of quitting among overwhelmed professionals.

The report’s release coincides with heightened apprehensions surrounding the risks posed by generative AI and the persistent challenge of ransomware attacks, indicating stress levels in the field have returned to levels observed during the peak of the COVID pandemic.
7 Reasons Why Generative AI Is Fueling Cyberattacks
Here are seven reasons why generative AI is fueling cybersecurity attacks.
1. Automated Attack Generation:
Generative AI empowers cybercriminals to automate the creation of sophisticated attack vectors. Traditional cyberattacks often required manual coding and execution, limiting the scale and speed of attacks. With generative AI, malicious actors can quickly generate tailored attack codes, thereby increasing the volume and efficiency of cyber threats. This automation allows them to target a larger number of potential victims simultaneously, overwhelming security systems and making detection more challenging.
2. Evasion of Defenses:
As cybersecurity measures evolve, cybercriminals also adapt their tactics. Generative AI allows attackers to develop novel methods that can evade conventional security mechanisms. By continuously generating variations of attack strategies, cybercriminals stay ahead of cybersecurity professionals who are tasked with defending against these threats.
This ongoing arms race between cybersecurity measures and cybercriminal tactics underscores the dynamic nature of the digital landscape. Generative AI, harnessed by malicious actors, presents a formidable challenge to traditional security approaches. Its ability to create sophisticated, ever-changing attack strategies demands a shift towards proactive and adaptive defense mechanisms.
To effectively counter these evolving threats, cybersecurity professionals must embrace AI-driven tools themselves, leveraging machine learning and advanced analytics to predict, identify, and mitigate potential attacks in real-time. Additionally, collaboration among organizations, sharing threat intelligence and collectively fortifying vulnerabilities, will be crucial in establishing a united front against the persistent innovation of cybercriminals.
3. Reduced Entry Barrier for Criminals:
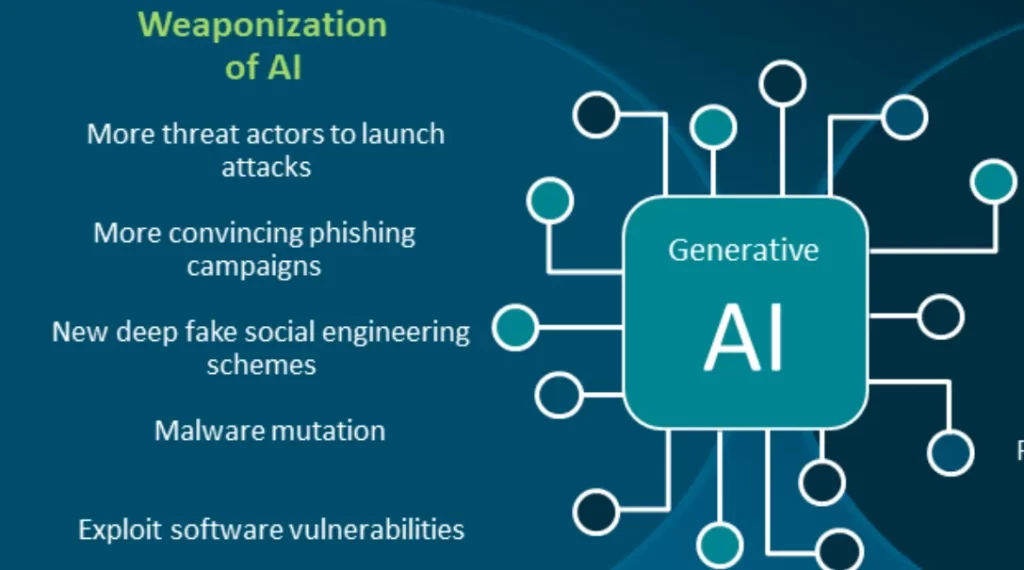
The accessibility of generative AI tools has lowered the entry barrier for cybercriminals. Previously, sophisticated attack techniques required extensive technical knowledge and coding skills. Now, with pre-built large language models and tools available, even individuals with limited technical expertise can launch advanced cyberattacks, contributing to the overall rise in cyber threats.
4. Customized Phishing Campaigns:
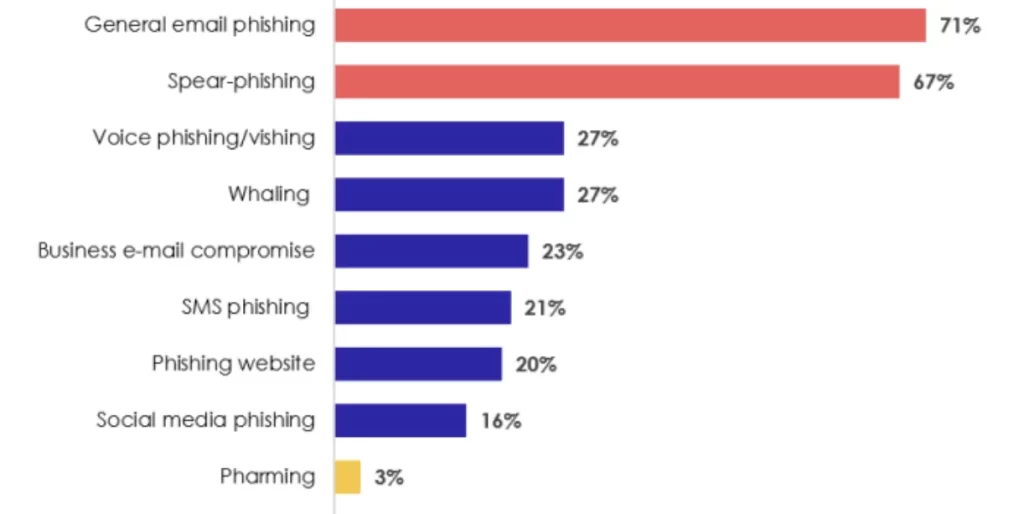
Phishing attacks have long been a favored tool in the cybercriminal arsenal. Generative AI takes this a step further by enabling the creation of highly personalized and convincing phishing emails. These emails can be tailored to mimic the writing style and preferences of the target, making them more difficult to identify as malicious.
5. Polymorphic Malware Creation:
Polymorphic malware is a type of malicious software that constantly changes its code to evade detection. Generative AI facilitates the rapid creation of polymorphic malware variants, making it challenging for traditional signature-based antivirus systems to keep up. This increases the risk of different types of malware infiltrating systems undetected.
The utilization of Generative AI in crafting polymorphic malware marks a significant shift in the landscape of cyber threats. By enabling the automatic generation of countless unique variations of malicious code, cybercriminals can effectively bypass static security measures that rely on fixed signatures for detection.
This dynamic and shape-shifting nature of polymorphic malware presents a daunting challenge for traditional antivirus systems, as their reactive approach struggles to adapt swiftly to the incessant stream of new and ever-evolving malware strains. Consequently, the potential for these agile and elusive threats to infiltrate systems undetected is amplified, underscoring the urgent need for cybersecurity strategies that harness AI-driven technologies to proactively identify and counteract these shape-shifting digital adversaries.

6. Data Poisoning and Misinformation:
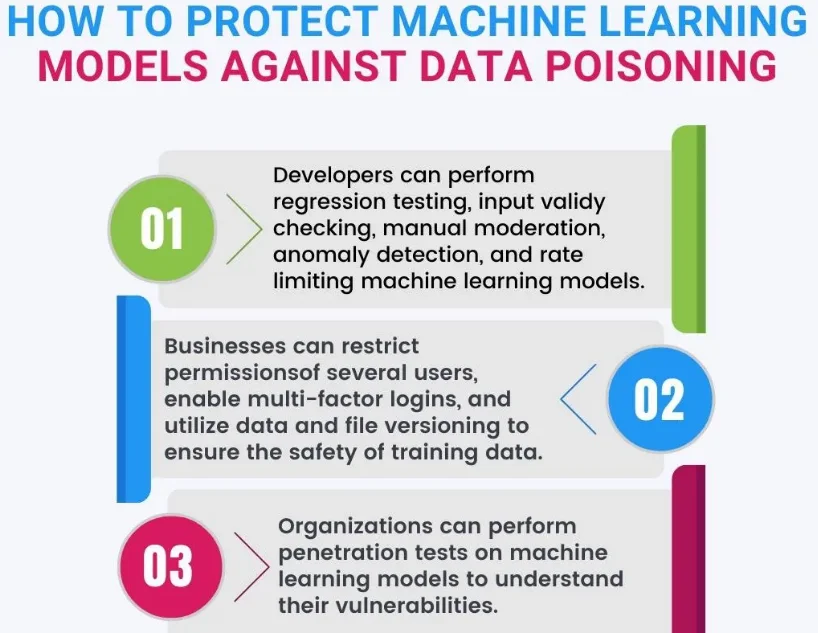
Generative AI can be utilized to produce fake data and content that appears authentic. This is particularly concerning in the context of misinformation campaigns and data poisoning. Cybercriminals can use AI-generated content to spread false information, compromise decision-making processes, and manipulate public perception.
7. Weakness Exploitation:
Generative AI aids cybercriminals in identifying vulnerabilities in software and systems. By generating massive amounts of simulated attacks, AI can identify weak points that might otherwise remain undiscovered. This enables hackers to exploit vulnerabilities before they are patched, leading to increased successful attacks.
Conclusion
The use of generative AI in cyberattacks is a double-edged sword. While AI technology has transformative potential for various positive applications, it also provides malicious actors with new tools to perpetrate cybercrimes on an unprecedented scale. The factors outlined in the CSO Online article clearly demonstrate why generative AI is fueling a significant rise in cyberattacks.
As we move forward, the cybersecurity landscape must evolve to counteract these threats effectively. This includes the development of AI-driven security solutions that can analyze and predict attack patterns, the continuous improvement of threat detection mechanisms, and international collaboration to combat cybercrime. By staying vigilant and adopting secure AI frameworks, the cybersecurity community can mitigate the risks posed by generative AI-powered cyberattacks and secure the digital world for future generations.
Which is the biggest reason why generative AI is leading to an exponential increase in cybersecurity attacks? Share it with us in the comments section below.





Add comment