The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving. As technology advances and attackers become more sophisticated, new cyber risks emerge. Organizations need to stay on top of the latest threats and prepare their cyber defenses accordingly. Damages from cybercrime will surpass the $10.5 trillion mark by 2025.
Ransomware attacks alone increased by 105% in 2021 compared to the previous year. Meanwhile, over 40 billion records were exposed in data breaches worldwide. Clearly, cyber threats are on an upward trajectory that demands urgent action from security leaders.

In 2024, new attack vectors and vulnerabilities will present even greater challenges. Staying ahead of emerging trends is crucial for effectively defending organizations’ digital assets. Understanding these predicted trends will enable organizations to get a step ahead of threat actors.
Companies that align security controls and policies with upcoming developments will have the best chance of detecting, preventing, and responding to attacks. With cyber risks rapidly evolving, a look at the future provides an indispensable opportunity to assess and bolster cybersecurity postures before the next big threat emerges.
This article explores the top 10 cybersecurity trends likely to dominate in the coming year, arming security professionals with actionable insights to prepare defenses.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Trends For 2024
Here are 10 key cybersecurity trends to watch out for in 2024:
1. Rise of Automated Cyberattacks
Advances in AI will enable cybercriminals to execute sophisticated automated attacks at massive scales including DDoS attacks. You can invest in DDoS protection services to protect your business from such attacks. Complex social engineering campaigns, personalized spear phishing emails, credential stuffing and content impersonation will be possible using AI. Developing AI-enabled cyber defenses and expertise in AI security will be crucial to counter this threat.

2. Increased Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware will continue to be a major threat, with attacks becoming even more frequent, sophisticated and costly. Attackers are shifting from mass distribution to precisely targeting victims using social engineering techniques. They are demanding higher ransom amounts, weaponizing data if not paid, and finding new ways to pressure victims into paying. Implementing strong endpoint security, training staff on phishing risks, and maintaining robust backups will be key to defend against ransomware.

3. Cloud Security Gets Priority
As cloud adoption accelerates, securing cloud environments becomes imperative. Organizations will focus on configuring cloud platforms securely, applying security controls to infrastructure-as-code, protecting data accessed via APIs, and managing misconfigurations which could lead to breaches. Tools such as Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) will gain prominence.

4. Growth of State Sponsored Attacks
Geopolitical tensions are motivating more sophisticated cyberattacks from nation-states. Disrupting critical infrastructure of hostile nations or stealing sensitive data will be a hot agenda for attackers. Attackers will leverage advanced persistent threat (APT) techniques making attacks harder to detect and attribute. Shoring up cyber defenses and collaborating with government agencies will help deal with this threat.

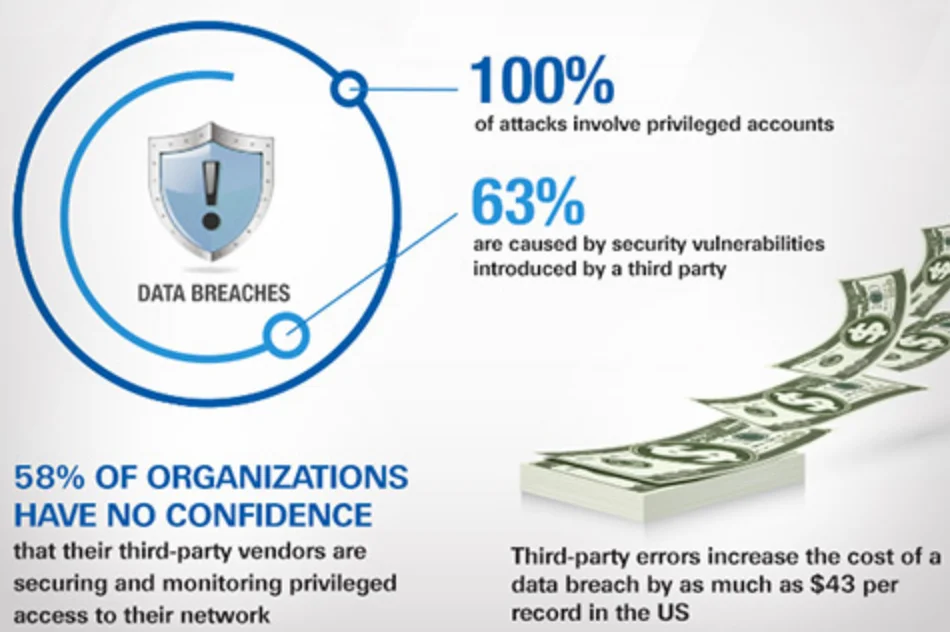
5. Targeting of Third Party Vendors
Attackers have realized that compromising third-party vendors provides access to their customers’ systems as well. Software supply chain attacks, targeting IT service providers or cloud vendors will increase. Organizations will need greater visibility into vendors’ security practices and integrate their cyber risk into enterprise risk management programs.
6. Emergence of Cyber-Physical Threats
As operational technology and industrial control systems connect online, new cyber-physical threats emerge. Attacks could target different industries and critical infrastructure like power grids, water systems and manufacturing plants with catastrophic impacts on human safety and the physical world. Securing industrial control systems, employee training and contingency planning will be key focus areas.
7. Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals
Demand for cybersecurity skills will exceed supply, with the talent crunch becoming more acute. Salary and poaching wars for qualified staff will intensify. Organizations must invest in training programs, align cyber roles to career growth prospects and develop talent internally to retain staff and close the cyber skills gap.

8. Privacy and Data Protection Regulations Expand
Governments will continue enacting data protection laws giving users more control over their personal data. Managing compliance to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA will be an ongoing challenge. Organizations will have to build data management programs adhering to ‘privacy by design’ principles and minimize personal data collection.
9. Evolution of Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance will cover more cyber risks but underwriting will also get stricter. Insurers will incentivize good cyber practices by tying premiums to policyholders’ security postures. Having robust controls and cyber preparedness will help obtain coverage at lower premiums. Cyber insurance budgets will need to be expanded.

10. Board Oversight of Cyber Risks
Boards of directors will take greater interest in cybersecurity given the rising financial and reputational impact of breaches. Information security leaders will need to measure their cybersecurity risk in financial terms and report security posture in business context to boards. Companies will create dedicated cybersecurity committees at the board level for oversight.

In summary, Cyberattacks are growing in scale and sophistication. Organizations will have to improve security across people, processes and technology fronts. Advanced technologies hold promise but also introduce new risks. Businesses will need to be nimble, collaborative and proactive in strengthening cyber defenses if they want to thrive in the face of these emerging threats. Following cybersecurity trends and best practices will allow companies to make strategic security investments and build cyber resilience.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity is a dynamic field that requires constant vigilance and adaptation. The threat landscape will no doubt continue evolving in 2024, bringing both new risks and opportunities. By planning ahead and aligning defenses with predicted trends, organizations can become more resilient. The top 10 trends outlined here provide a valuable roadmap for security leaders looking to strengthen their security postures in the face of future threats. While unknown dangers always loom, foresight and proactive preparation will ensure organizations have the capabilities needed to detect and respond to attacks. Cybersecurity may be a perpetual challenge, but staying informed on the latest developments will enable businesses, government entities and individuals alike to meet the threats of tomorrow.
Which cybersecurity trend will create the biggest impact in 2024 in your opinion? Share your opinion with us in the comments section below.





Add comment